An international research team has discovered that the IFT20 protein helps some cancer cells to invade by facilitating the transportation of membranes and proteins within parts of the cell.
Primary cilia exist on the surface of almost all human cells, acting as “cell antenna” that receive information from outside the cell. IFT20 (intraflagellar transport 20) is a protein present in most human cells that plays an essential role in the formation and functions of these primary cilia. In healthy cells it acts as a “cargo adaptor” to transport proteins along microtubules within cilia, but many cells lose these cilia when they become cancerous. This research has shed light on the function of IFT20 in non-ciliated cancer cells for the first time. The discovery has potential applications for developing new cancer treatment methods that block invasive cancer cells by targeting IFT20. The findings were published on January 26 in the online edition of Scientific Reports.
This research was carried out by an international team including Associate Professor NISHITA Michiru (Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine Department of Physiology and Cell Biology), Professor MINAMI Yasuhiro (Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine, Department of Physiology and Cell Biology), Professor Victor W. Hsu (Harvard Medical School) and Professor Gregory J. Pazour (University of Massachusetts Medical School).
Most cancer-related deaths are said to be caused by cell invasion and the consequent spread of cancer cells to other parts of the body (metastasis). To counter this, scientists are searching for the mechanism that controls the invasive properties of cancer cells.
Researchers already knew that a cell membrane protein known as Ror2 expresses highly in various cancer cells, and it promotes cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Professor Nishita’s team investigated various kinds of non-ciliated cancer cells and discovered that Ror2 promoted cancer cell invasiveness by inducing the expression of IFT20.
Many tumor cells break through the barrier of the extracellular matrix and infiltrate their surroundings by forming protruding structures known as invadopodia (see figure). The formation of invadopodia requires membranes and proteins supplied by the intracellular transport system, using the Golgi complex. The Golgi complex must be close to invadopodia to deploy these materials. The team’s findings demonstrate that in tumor cells, IFT20 induces the Golgi complex to form microtubules by promoting interaction between the Golgi proteins GM130 and AKAP450. It also regulates the structure of the Golgi complex and transport of proteins within the complex. “This research has clarified a new molecular mechanism related to the formation of Golgi-derived microtubules, and its important role in invasive cancer cells,” said Professor Nishita.
The relationship between loss of cilia and a cell’s cancerous properties remains unclear. IFT20 is involved in the formation and function of cilia in healthy cells, but in non-ciliated cancer cells it is now clear that IFT20 is responsible for the formation of invadopodia. By continuing to analyze the relationship between IFT20 and the loss of cilia, this line of research could help shed light on the fundamental question of why many cancer cells lack cilia. Additionally, if the specific regulatory mechanism of IFT20 in cancer cells is revealed, this knowledge could be used to develop treatment that targets IFT20 to block invasive cancer cells.
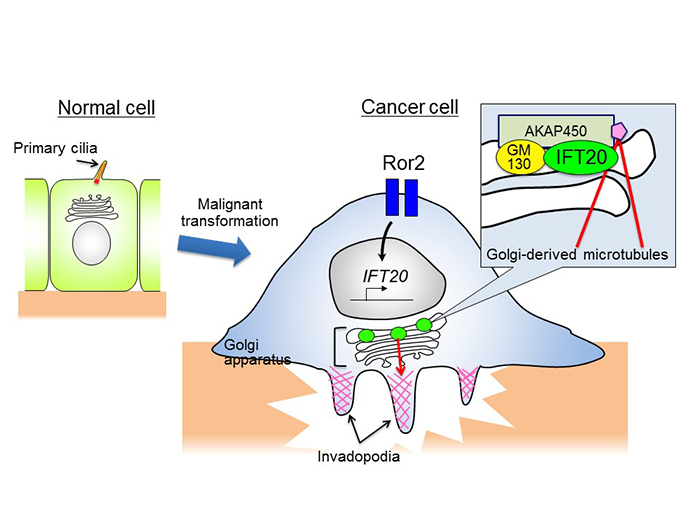
In healthy cells IFT20 regulates the formation and function of primary cilia. Many cancer cells lack cilia, and these cells induce and sustain the expression of IFT20 through the high expression of Ror2. IFT20 promotes the formation of Golgi-derived microtubules by binding with the GM130-AKAP450 complex in Golgi. By doing this it regulates the deployment of Golgi and transport of proteins within Golgi, both important parts of the formation of invadopodia.
Journal information
- Title
- “Ror2 signaling regulates Golgi structure and transport through IFT20 for tumor invasiveness”
- DOI
- 10.1038/s41598-016-0028-x
- Authors
- Michiru Nishita1, Seung-Yeol Park2, Tadashi Nishio1, Koki Kamizaki1, ZhiChao Wang1, Kota Tamada3, Toru Takumi3, Ryuju Hashimoto4, Hiroki Otani4, Gregory J. Pazour5, Victor W. Hsu2, Yasuhiro Minami1
- Division of Cell Physiology, Department of Physiology and Cell Biology, Kobe University, Graduate School of Medicine
- Division of Rheumatology, Immunology and Allergy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical School
- RIKEN Brain Science Institute
- Department of Developmental Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Shimane University
- Program in Molecular Medicine, University of Massachusetts Medical School
- Journal
- Scientific Reports