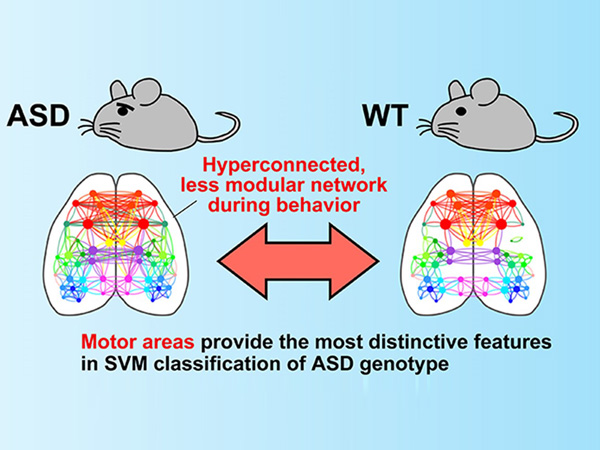
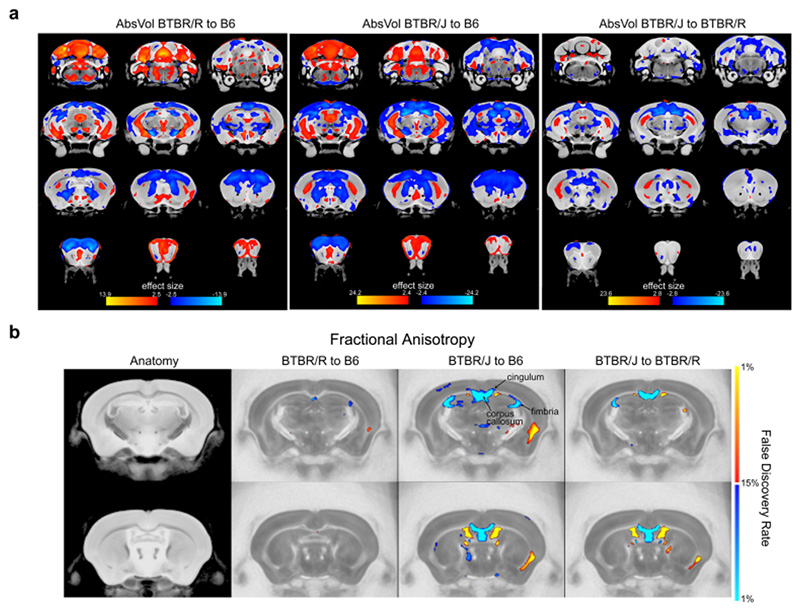
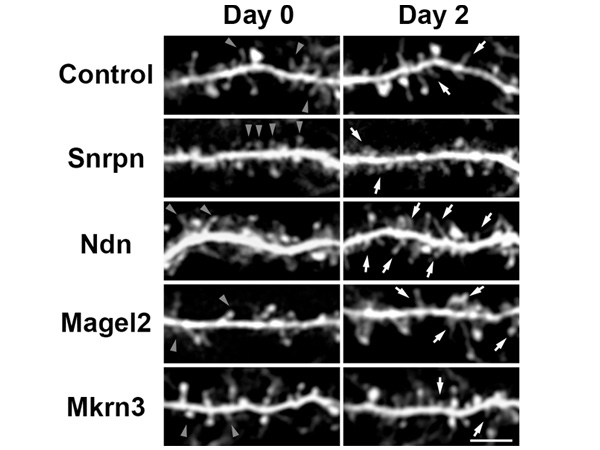
Autism is difficult to study and more difficult to treat because it is an individual condition lacking precise quantification. The development of mouse models of human mental disorders has proven a tractable approach to studying the molecular mechanisms, a new review argues and highlights the current state of the art in autism research.

©NAKAI Nobuhiro (CC BY)
Whether or not the autism spectrum is a disorder to be treated or a disability to be accommodated is debated by experts. This, however, is symptomatic for the fact that it is a very individual condition that has many expressions as well as causes, with no quantitative evaluation system or objective, mechanized diagnostic method. This makes it hard for researchers to analyze the autism’s mechanisms and develop potential treatments. Kobe University Professor of Physiology and Cell Biology TAKUMI Toru explains the situation: “Autism is a complex disorder like cancer. Although genetic causes contribute to the disorder more than other mental disorders, environmental causes are also important. To treat autism, we need to understand the neural circuits of social maladaptation and develop new technologies to manipulate neural circuits in humans.”
One such technology is the development of mouse models of human mental disorders, of which Takumi is a pioneer. Genetically modified mice that exhibit social behavior disorders offer a unique opportunity to accurately analyze the molecular and physiological mechanisms behind autism and to test potential treatment approaches. An internationally recognized expert in the field, Takumi was invited by the journal Molecular Psychiatry to summarize the state of the art.
In the review, the neuroscientist stresses the importance of the insular cortex, a deeply buried region of the brain that has reciprocal connections to sensory, emotional, motivational and cognitive systems. In mice, it is involved in the regulation of emotions, empathy, and motivation amongst many other functions, and in humans it is known to be involved in self-awareness. The review explains in detail which genes and physiological functions of the insular cortex affect the emergence of autism. “Psychiatric disorders, in general, are considered to be neurocircuit disorders, and therefore, the elucidation of the neural circuitry in social behavior will lead to the development of future neurocircuit-based therapies,” explains Takumi.
One intriguing method to study how molecular dysfunctions cause social maladaptation is what Takumi calls the “mouse metaverse”: “We have recently developed a virtual reality (VR) system to record neural network activity during social behavior. Combining two VR systems opens a new avenue for exploring inter-brain dynamics.”
With his work, the Kobe University professor ultimately tries to understand the molecular basis of the brain’s mental function. “We are interested in the human mind. Through understanding the pathophysiology of autism, I’d like to understand how the human mind is generated in the brain,” says Takumi.
Acknowledgments
The authors receive financial support from JSPS, the Taiju Life Social Welfare Foundation, the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, the Japan Science and Technology Agency, the Intramural Research Grant for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders of NCNP, the Takeda Science Foundation, the Research Foundation for Opto-Science and Technology, the Naito Foundation, the Tokumori Yasumoto Memorial Trust for Researches on Tuberous Sclerosis Complex and Related Rare Neurological Diseases, and the Canada Research Chairs Program.
Original publication
Sato et al.: Social circuits and their dysfunction in autism spectrum disorder. Molecular Psychiatry (2023). DOI: doi.org/10.1038/s41380-023-02201-0